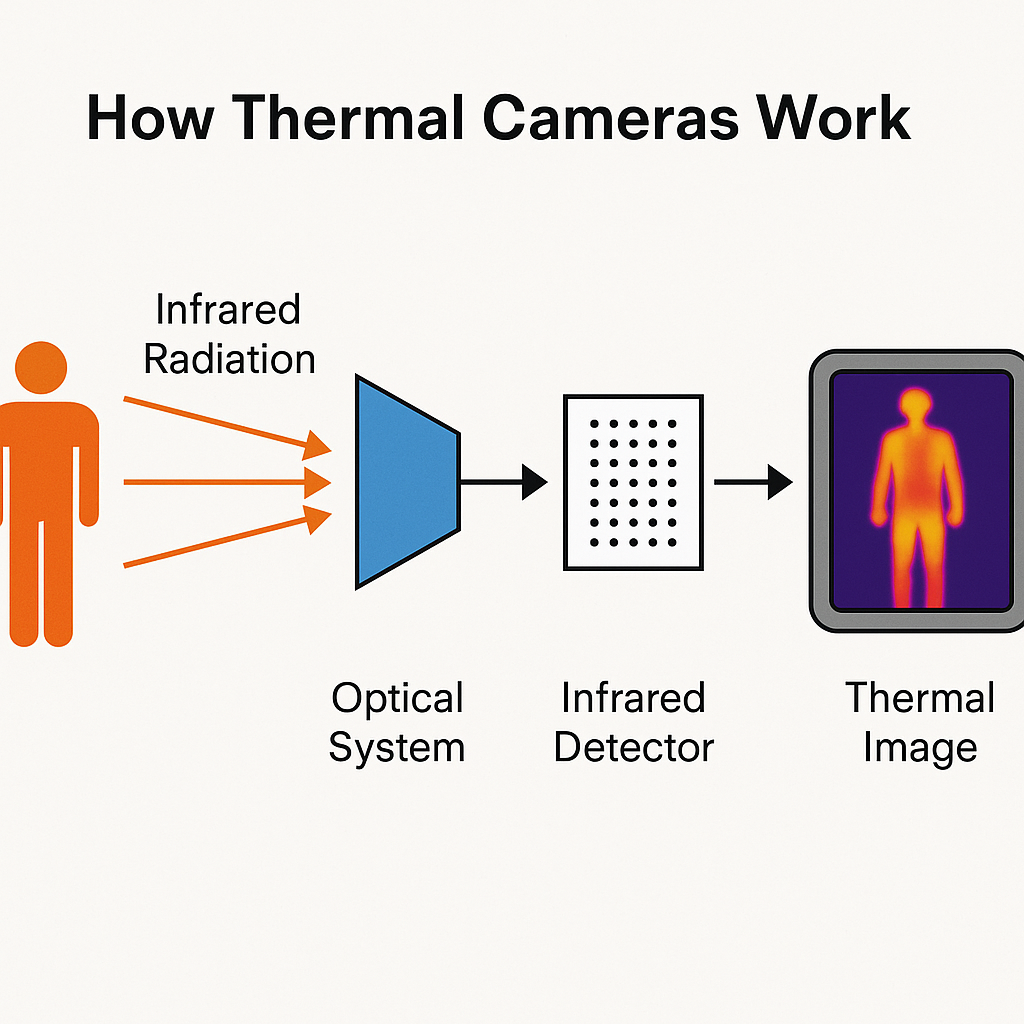
Thermal imaging is no longer confined to high-end research labs or military-grade surveillance. Today, this technology has become a cornerstone of industrial maintenance, energy audits, and predictive diagnostics. By converting invisible infrared (IR) radiation into visible, interpretable images, thermal cameras allow us to see heat—a capability with profound implications for safety, efficiency, and asset reliability.
Every object above absolute zero (-273.15°C) emits infrared radiation proportional to its temperature. Thermal imaging devices capture this radiation and translate it into a visual representation called a thermogram. Unlike standard photography, which relies on reflected visible light, thermal imaging detects emitted energy, making it effective even in total darkness or through certain obscurants like smoke and light fog.
Electrical Systems: Identify overloads, unbalanced phases, or impending breaker failures before catastrophic shutdowns.

Mechanical Equipment:Detect abnormal bearing friction, misalignment, or lubrication failure.
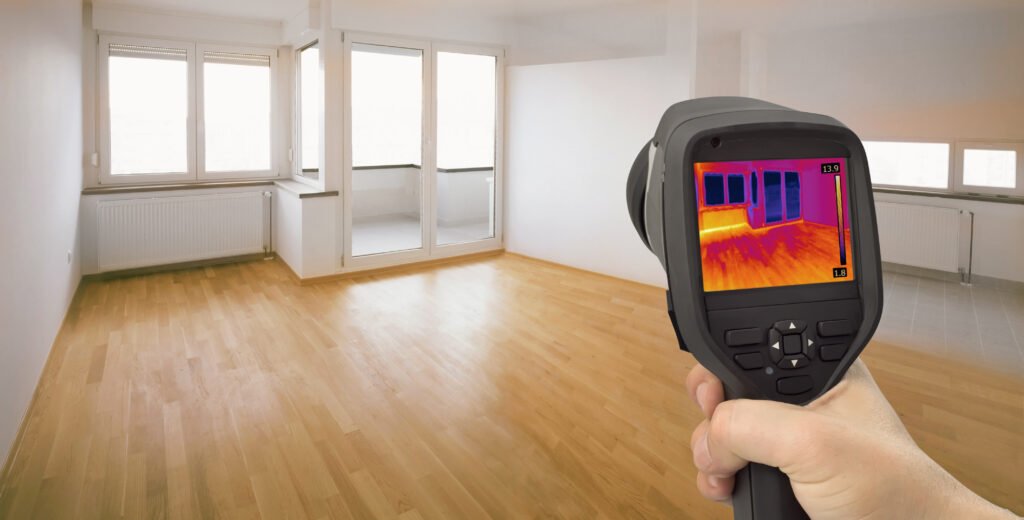
Building Performance: Locate insulation voids, HVAC inefficiencies, and air leaks to optimize energy usage.

Safety & Security: Monitor high-risk areas, detect intruders by heat signature, and support emergency response in low-visibility conditions.

Knowing how a thermal imager works enhances the accuracy of inspections and the credibility of reports. Factors like emissivity, reflected temperature, and environmental conditions directly impact measurement quality. Skilled thermographers apply these principles to ensure reliable data interpretation and actionable results.
Thermal imaging turns invisible energy patterns into actionable insight. Whether you’re diagnosing an overheating motor, conducting an energy audit, or improving plant safety, understanding the mechanics of thermal cameras allows you to maximize their potential. As industries continue to shift toward predictive maintenance and energy efficiency, thermal imaging is no longer optional-it’s a critical tool in the modern diagnostic arsenal.
Need thermal growth analysis or precision shaft alignment? Contact THERMOInspect for expert services with advanced laser and infrared diagnostic tools.