Infrared (IR) cameras are advanced imaging devices designed to detect and visualize heat energy – infrared radiation – emitted by objects.
Unlike standard cameras that capture visible light, IR cameras translate temperature differences into a thermal image, allowing users to “see” heat patterns that are otherwise invisible to the human eye.
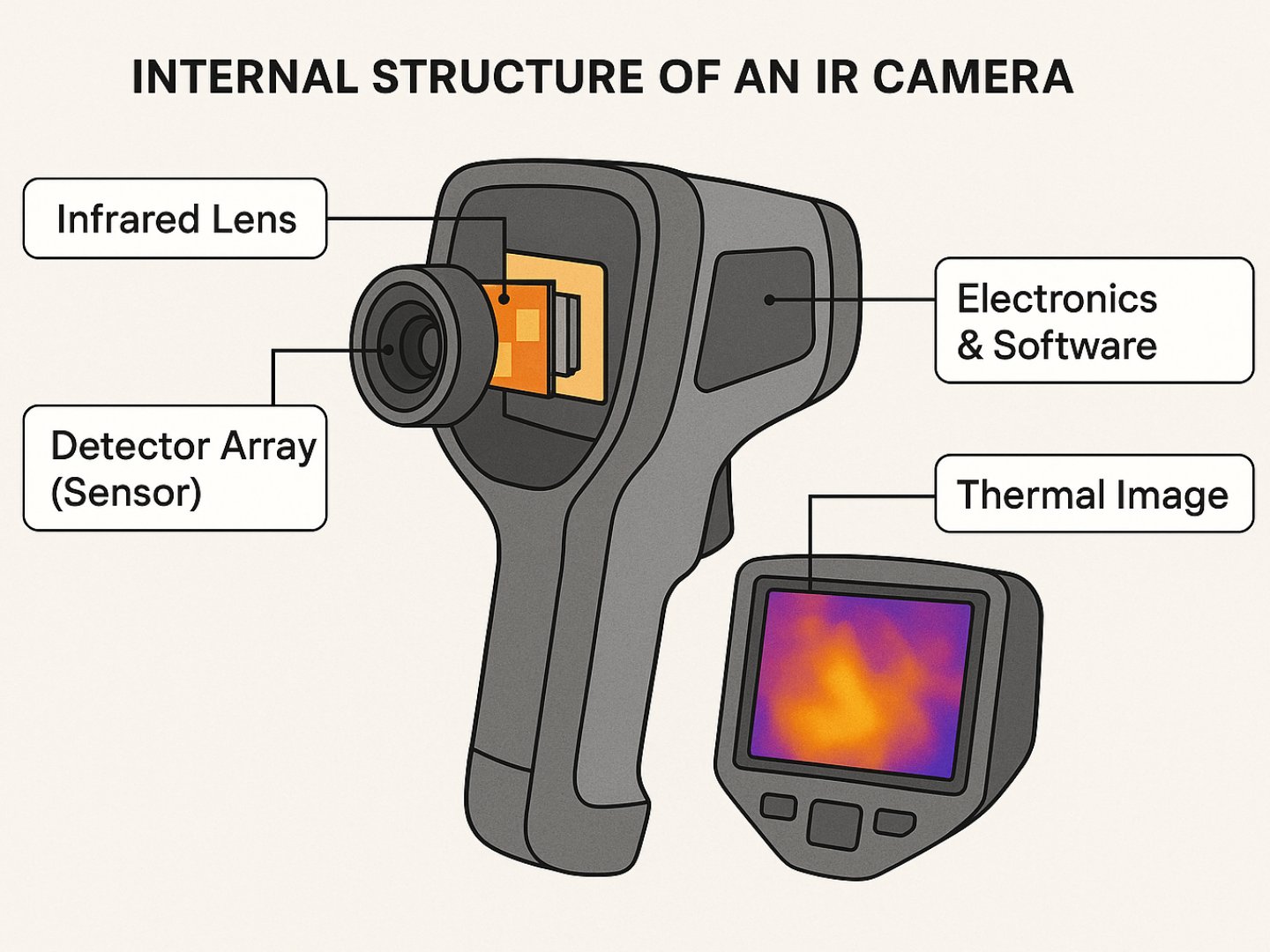
An IR camera consists of three primary components:
Modern IR cameras also include features like high-resolution displays, Wi-Fi connectivity, and advanced analysis tools for precise measurement and reporting.
Infrared cameras are categorized based on their wavelength sensitivity and application:
Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR) – 8 – 14 µm range, commonly used for electrical inspections, building diagnostics, and general industrial maintenance.
Mid-Wave Infrared (MWIR) – 3 – 5 µm range, ideal for high-temperature applications such as furnace monitoring or aerospace testing.
Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR) – 0.9 – 1.7 µm range, used in research, manufacturing, and specialized imaging tasks.
They also vary by form factor, including handheld, fixed-mount, and drone-mounted units.
Well-known manufacturers include FLIR Systems, Fluke, Testo, Keysight Technologies, and Optris, each offering models tailored to different industries, from electrical maintenance to scientific research.
In modern industry, infrared cameras have become indispensable tools for predictive maintenance, safety assurance, and quality control – empowering professionals to make informed, data-driven decisions.
Need infrared imaging services? Contact THERMOInspect for expert services with advanced laser and infrared diagnostic tools.